Cell Regulation
Keywords: cell signalling, ADP-ribosylation, glycerophosphoinositols, membrane transport, inflammation, cancer, drug discovery, cellular imaging.
Group leader: Daniela Corda
Contacts:
Phone: +39 0816132536
Lab: +39 0816132495
Email: daniela.corda@cnr.it
The major contributions of the laboratory are in the field of signalling and membrane traffic.
Our group has pioneered the field of protein ADP-ribosylation, by demonstrating the physiological roles of this post-translational modification and identifying the cellular substrates of ADP-ribosyl transferases. An important accomplishment, among others, has been the identification and characterization of BARS (Brefeldin-A ADP-ribosylated substrate; CtBP1-S), a protein that plays a central role in the processes of membrane fission, as well as in cell division and in growth and apoptosis. Membrane fission is a regulator of cell division through its key role in the "mitotic Golgi fragmentation and check point" process. BARS has therefore been investigated as a druggable component of the cell-division machinery.
This has led to pharmacological developments, with the identification (by molecular modelling, virtual screenings and biochemical validations) of small molecules binding the Rossmann fold pocket in BARS, that are able to interfere with tumour growth and spreading and are being studied as novel anticancer drug leads.
Other aspects related to the ADP-ribosylation field are the design of a method for the identification of the ADP-ribosyl-proteome, and the definition of the enzymes involved in this post-translational modification, along with their regulation. Our group has defined the role of endogenous ADP-ribosylation in membrane transport. Here, we have deciphered the regulatory mechanism mediated by the PARP12 enzyme that modifies specific substrates, such as members of the Golgin and Rab families, key players in the exocytic and endocytic pathways, respectively.
Along a different line, the laboratory has identified and characterized a new class of bioactive phosphoinositide metabolites, the glycerophosphoinositols, which are now recognized cell mediators. Our work is now centered on the role of these compounds in immune and inflammatory responses in lymphocytes as well as on the use of the glycerophosphoinositols as anticancer drugs (leads) based on their effects on the invasive potential of tumour cell lines.
In summary, a common ongoing pattern throughout our studies is the focus on understanding the mechanisms of different cellular functions in normal and diseased states, with the aim of exploiting this knowledge for the development of novel pharmacological tools.
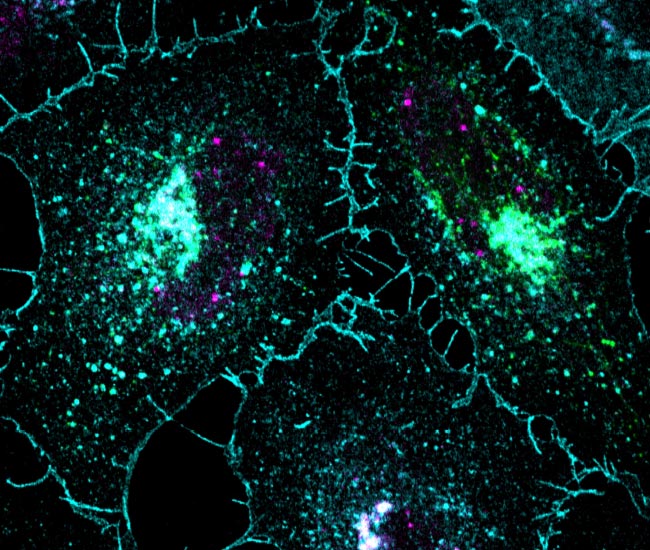
PKD-dependent PARP12-catalyzed mono-ADP-ribosylation of Golgin-97 is required for E-cadherin transport from Golgi to plasma membrane.
PNAS, 119(1), 2022
Grimaldi G, Filograna A, Schembri L, Lo Monte M, Di Martino R, Pirozzi M, Spano D, Beccari AR, Parashuraman S, Luini A, Valente C, Corda D.
The phosphatase Shp1 interacts with and dephosphorylates cortactin to inhibit invadopodia function.
Cell Commun Signal. 2021, 19(1):64
Varone A, Amoruso C, Monti M, Patheja M, Greco A, Auletta L, Zannetti A, Corda D.
Molecular mechanism and functional role of brefeldin A-mediated ADP-ribosylation of CtBP1/BARS.
PNAS, 110(24):9794-9
Colanzi A, Grimaldi G, Catara G, Valente C, Cericola C, Liberali P, Ronci M, Lalioti VS, Bruno A, Beccari AR, Urbani A, De Flora A, Nardini M, Bolognesi M, Luini A, Corda D.
A 14-3-3γ dimer-based scaffold bridges CtBP1-S/BARS to PI(4)KIIIβ to regulate post-Golgi carrier formation.
Nat Cell Biol. 2012, 14(4):343-54
Valente C, Turacchio G, Mariggiò S, Pagliuso A, Gaibisso R, Di Tullio G, Santoro M, Formiggini F, Spanò S, Piccini D, Polishchuk RS, Colanzi A, Luini A, Corda D.
Mitotic Golgi partitioning is driven by the membrane-fissioning protein CtBP3/BARS.
Science. 2004, 305(5680):93-6
Hidalgo Carcedo C, Bonazzi M, Spanò S, Turacchio G, Colanzi A, Luini A, Corda D.
Researchers:
Simone Di Paola s.dipaola@ieos.cnr.it
Giovanna Grimaldi g.grimaldi@ieos.cnr.it
Alessia Varone a.varone@ieos.cnr.it
Technologist
Nina Dathan n.dathan@ieos.cnr.it
Lab manager
Maria Matarese m.matarese@ieos.cnr.it
Post-doc fellow:
Marcello Monti m.monti@ieos.cnr.it
PhD Student
Anupama Pavithran a.pavithran@ieos.cnr.it
The funding obtained as Research Group or as Coordinator of collaborative applications includes:
MIUR - PRIN: Integration of cutting-edge spectroscopic and imaging techniques for the structural analysis of living-cell machineries from the atomic to the cellular level;
Progetto Medintech: Mechanisms of the enhanced inflammatory responses in ageing individuals: inflammageing.
Progetto BioForIU: PARP12-dependent mono-ADP-ribosylation controls specific membrane transport routes- a functional and morphological analysis.
Departmental project: SerGenCOVID-19. Indagine sierologica e genetica CNR sull’immunità e suscettibilità all’infezione da SARS-CoV-2 e creazione di una biobanca;
Regional project (POR) SATIN: Sviluppo di Approcci Terapeutici INnovativi per patologie neoplastiche resistenti ai trattamenti;
Regional project (POR) CIRO: Campania Imaging Infrastructure for Research in Oncology;
Contracts with Industrial Partners: 1. La fosfatasi shp1 e i suoi leganti, i glicerofosfoinositoli, nell'identificazione e sviluppo di terapie specifiche contro il tumore; 2. Bio-metabolism and/or mechanism of action, as determined by the most appropiate technologies (such as bioimaging, imaging-mass- spec or biochemistry) of the lead compounds and molecules of interest;
Individual Grant AIRC/FIRC: The CtBP/BARS involvement in tumor progression: a specific target for pharmacological intervention;
PRONAT II project: Identification of bioactive products of natural origin;
MIUR: FaReBio di Qualità: Farmaci e Reti Biotecnologiche di Qualità genetica, medicina
predittiva e nutraceutica, sviluppo di diagnostici e farmaci innovativi;
MIUR, Progetto di Interesse Invecchiamento: Innovazioni tecnologiche e molecolari per il
miglioramento della salute dell'anziano;
Progetto Bandiera Epigenomica: Il Bioimaging per lo studio dell'architettura nucleare in
epigenetica;
MIUR-PON01: Antigeni e Adiuvanti per Vaccini e Immunoterapia;
MIUR-PON01: Una piattaforma tecnologica integrata per lo sviluppo di nuovi farmaci per malattie
rare.